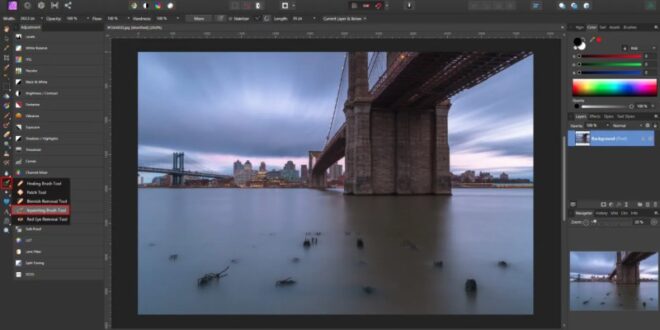
Step By Step Guide To Using The Healing Brush For Photo Retouching – Follow these 10 steps to retype your photos. This is one of the best and easiest ways to edit images.
Have you ever noticed pictures of flawless models in magazines and on billboards? And how to perfectly restore the skin in Photoshop? This tutorial will show you how to touch up skin like a Photoshop pro and get the perfect results for your photo.
Step By Step Guide To Using The Healing Brush For Photo Retouching
Updating a professional skin in Photoshop doesn’t have to be a complicated process, the more efficient it is, the better. The more results the better. Have you ever noticed pictures of flawless models in magazines and on billboards? And think about how you can achieve that amazing, perfect editing yourself? In addition, this tutorial will show you how to soften the skin in Photoshop and get the perfect visual effect for you.
Frequency Separation Retouching Tutorial In Photoshop
He deals with minor issues, hair, blemishes and evens out the skin tone. These small changes will make a big difference in the final image result. Photography is important, though. After shooting or editing after making a difference to the image. Do you want your photos to look unique and have natural tones So this tutorial is designed for you to learn how to edit skin in Photoshop.
In the steps below you’ll learn how to give your sketches a smooth, natural-looking skin and a professional skin retouch in Photoshop.
From the toolbar, select the Spot Healing Brush and set the Type option to ‘Context Information’ from the top toolbar.
Erase the spots by clicking on the image, and Photoshop will quickly heal the spots and give the skin a soft texture. You can adjust the brush size to be slightly larger than the stain for better results.
Skin Retouching In Photoshop Using Frequency Separation (5 Steps)
Please note that while removing blemishes Keep it natural, like getting rid of pimples, acne, or minor problems, it is best not to remove the permanent ones. Because it will make the image beautiful and realistic. and reveal their identity
Make a copy of the existing layer where you have corrected the stain to make the skin lighter and softer.
Use the ‘High Pass Filter’ to smooth the surface by going to Filter > Other > High Pass and setting the High Pass Radius to 10.
Select the brush tool and set the color to white. Make sure the Blend Mode is Normal, the Opacity is 100% and the Flow is 100%, then show the sickening effect on the skin. You can also go to Filter > Noise > Dust & Scratches.
How To Edit A Photo In Photoshop? Photo Touch Up
Check the layer mask and check if the smoothing effect is good enough. Or you can reduce the opacity of the mask layer to your liking.
Professional skin correction in Photoshop helps your photos capture attention by bringing subtle changes for example, skin retouching helps avoid distractions such as hair loss, wrinkles, spots, etc and is important.
Research has found that 5.3 billion photos are taken worldwide each day. And only a few pictures got the attention they deserve. Only the most impressive images will stand out from the crowd. Therefore, updating the professional skin in Photoshop is very important.
Updating a professional skin in Photoshop can undoubtedly be a complicated process for you. If you do this first, even a small edit may require several layers to achieve the result. So having a basic knowledge of Photoshop layers can help you learn quickly as well, we are sure that the steps above are enough to get you started with skin smoothing in Photoshop.
Creative Portrait Editing Techniques: Ultimate Guide
There are many ways and techniques to retouch any type of product or image, but Photoshop can help save lives when it comes to image editing. It provides you with a wide range of Photoshop elements to work with.
UK Clipping Path will edit two of your images for free. It allows you to check if the images meet your expectations or not. One of the most important tools in Photoshop is the Healing Brush Knowing how to use the Healing Brush in Lightroom is essential for anyone who wants to remove blemishes, spots, or unwanted objects from their photos. This tool makes the image recovery process easy. This helps ensure that the final photos look natural and flawless.
It works by allowing the user to paint over imperfections. which are then replaced by pixels from the surrounding area. and make the colors blend properly This is especially useful for portrait photographers who want to emphasize the skin. The same goes for landscape photographers who want to remove distractions from their photos.
By learning the Healing brush in Lightroom, you can ensure that your images look natural and professionally cleaned. Here are the steps to guide you through this:
How To Retouch Skin Using Frequency Separation In Photoshop
When using this feature in landscape photography it is necessary to choose the right place for editing. Look for distractions such as specks of dust, debris, or other unwanted objects that clutter the space. It’s great for small edits like this, helping you keep your landscape looking natural.
Adjusting the settings in Lightroom is important to get the best results. Adjust the size of the brush to match the blemishes you want to erase. This step is important to ensure that the editing does not stop and look fake.
Want to use Lightroom’s storage tools effectively? Click and drag to the area you want to edit. The device automatically samples pixels from the surrounding area. and blend those pixels to hide imperfections. This technique is especially useful for correcting small problems, such as vision spots or small horizontal spots.
After using this Zoom in for a closer look at the edited area. Make sure the editing blends naturally with the rest of the image. If necessary, adjust the lighting or reapply to blend well. This careful inspection results in a flawless final image.
How To Remove Lines In Photoshop
For better results, instead, combine the Heal Brush with other post-processing tools in Lightroom, adjusting the aspect ratio of the photo can help remove unwanted elements. Additionally, use the tool to enhance the look of the landscape. This ensures that every detail contributes to stunning photos.
Here is a list of some important Lightroom features that can help you edit your images better:
Learning how to use the Healing Brush in Lightroom will greatly improve your photo editing skills. This allows smooth deletion of bugs.
Having an even skin tone can make a huge difference in a portrait. Once the target area is selected, adjust the values gradually to correct any discrepancies. This process must be done carefully to maintain a natural look. If you encounter any problems Use the Visualize Spots feature to identify and fix defects. For those using the premium version, more advanced tools will be available for more detailed processing.
Remove Dark Circles Under Eyes: Photoshop
Reducing blemishes is a common requirement for image enhancement. After opening your photo in Lightroom, make sure the correct settings are used to focus on specific areas without processing the entire image. You can try using Adobe Photoshop for more customization. Always keep a consistent perspective on the final image to ensure a natural look.
Enhancing facial features involves minor adjustments to emphasize the subject’s natural beauty. Use the tool to make small corrections around the eyes, nose, and mouth. Always zoom out to get a wider view of the full effect. and ensures consistency throughout the drawing. If you’ve joined any Lightroom community, share your work and gather feedback from other members.
Lighting can have a huge impact on the quality of a portrait. Adjusting exposure and contrast can solve many lighting problems, such as low-light situations. When doing this Make sure the changes blend well with the rest of the image. If you encounter an issue that cannot be fixed within Lightroom, sometimes it may be necessary to switch to a different version of the software or use additional tools.
Before it’s finished Look at the full picture for areas that may need minor adjustments. This includes making sure all changes are compatible and that no new issues appear, whether you’re using the free version or have access to premium features. Learning these techniques will greatly improve your skills. Be sure to check messages from the software for any updates or additional features that may help with this process.
How To Use Healing Brush In Lightroom: A Comprehensive Guide
Creating a Healing Brush in Lightroom can greatly improve your photo editing skills. But many common mistakes can hinder your progress. By avoiding these mistakes you can be sure that your images look professional and beautiful.
One of the most common mistakes is using too many tools. Although fixing every small bug can be difficult. But doing so can make the image look unnatural. It is important to keep the natural look and feel of the photo to avoid over editing the look.
Failure to adjust these settings can cause negative results. The size, hair, and opacity of the brush must be adjusted for each area you are working on, for example, using a larger brush for smaller imperfections than intended. While a small brush may not cover the area well enough.
When the device takes samples from an inconsistent location it can cause color and texture damage.
 Alveo Creative Blog Guiding users through techniques for enhancing images, retouching portraits, and mastering popular editing software
Alveo Creative Blog Guiding users through techniques for enhancing images, retouching portraits, and mastering popular editing software